Internet Networking slides |
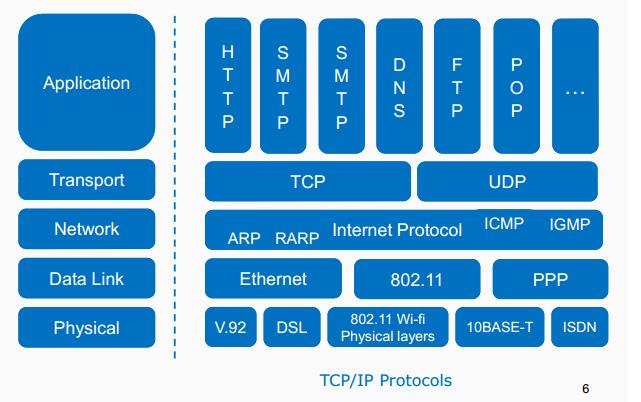
Review of the communications and networking stack
Clients and Servers
- Both are computers, depends on their purpose
- Networking’s purpose is to get ‘data’ from one to the other
- …. even when they are on the other side of the world
Take a look at
$ ping brandeis.edu
$ traceroute brandeis.edu
Basic Terms
- Host: On the internet, a computer that is part of the network is often referred to as a
host - MAC address: A totally unique number assigned at time of manufacture to every piece of hardware that can be connected to the network. Media Access Control address. It “cannot” be changed.
- IP Address: Internet Protocol Address, e.g. 12.44.23.123
- Domain name: A name assigned to a host on the internet, e.g. brandeis.edu
- DNS: Domain Name System. An internet-wide service (a distributed database) that associates ip addresses to domain names
MAC addresses, IP addresses and DNS
- User types in a domain name
- Target computer is identified by an IP address
- So: Need a phonebook of some kind
- DNS: distributed name service
Basic Network utility programs
- ping: sends a message to a destination host and listens that the packet is sent back
- traceroute: similar, but records the intervening hosts
- ifconfig: list network interfaces and what IP address they are associated with
- netstat: A really verbose printout of all the local TCP/IP ports and whats going on
- nslookup: Look up the ip address of a domain name
- whois: lookup what the internet knows about the owner of a certain domain name
More about IP
- So the IP address is for 1 specific ‘host’ or server (as usual there are exceptions :)
- IP is the way servers talk ‘to each other’ to get a packet of bits between them
- Conceptually, ‘send these bits to this ip address’
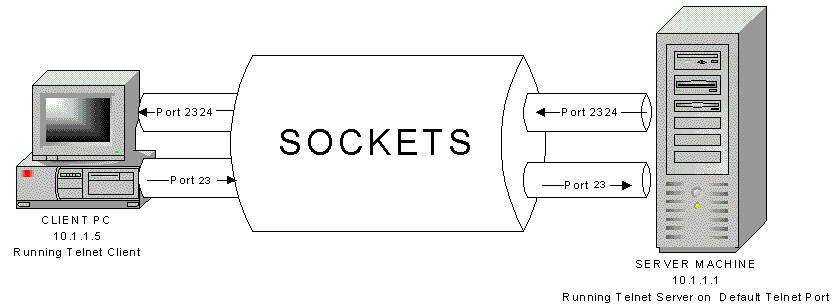
- What’s a port number
- TCP/IP: what it means